Lire l’article original. 1, 2, 3, 4 : comment adopter le bon tempo ? Pourquoi le son est-il meilleur dans une salle de concert que dans notre salon ? Pourquoi les styles musicaux ont des battements par minute (bpm) différents ? En quoi le rythme musical, ses fréquences et ses harmonies, sont des grandeurs mathématiques […]
Publications
First time featured in the Computer Music Journal!
From a facebook post by Marco Fiorini First time featured in the Computer Music Journal! 📚On this issue, the seminal article on Somax2 by Gérard Assayag, Laurent Bonnasse-Gahot and Joakim Borg is finally out, and I’m appearing as contributor to the tutorials and documentation! 🙏The journal gives also a nice overview of the Erc Reach […]
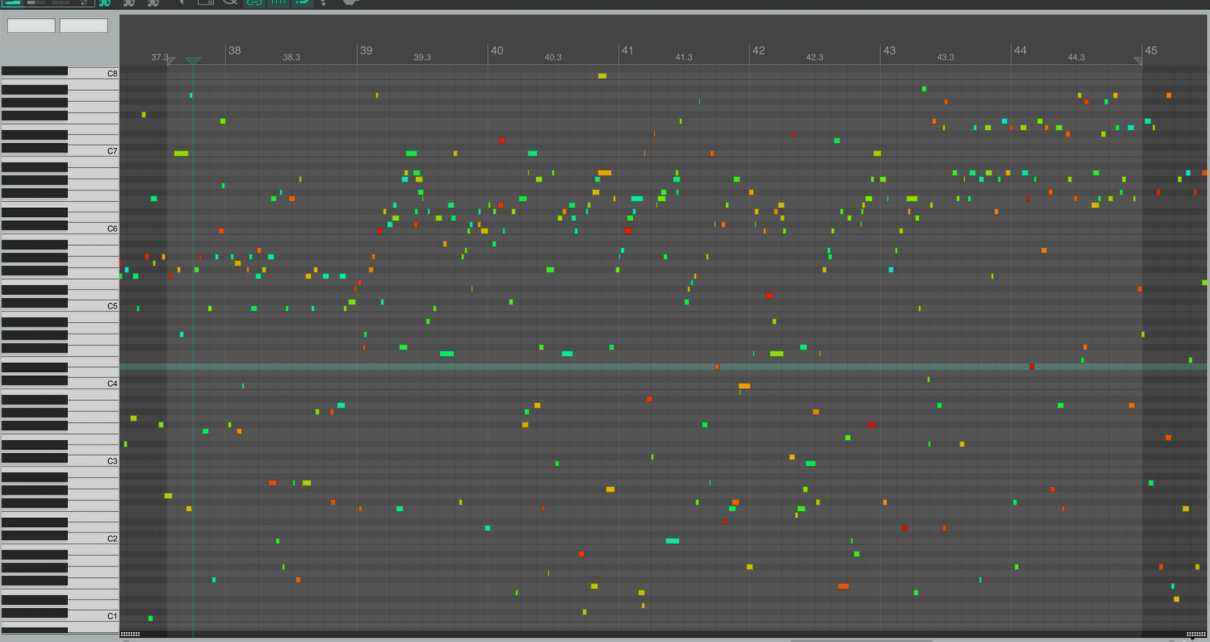
The corpus’ body. Embodied Interaction from Machine-Learning in Human-Machine Improvisation.
Article by Pierre Saint-Germier (CNRS, STMS – IRCAM), Clément Canonne (CNRS, STMS – IRCAM) and Marco Fiorini (STMS – IRCAM, Sorbonne Université, CNRS) has been accepted for the AIMC2024 Conference (The International Conference on AI and Musical Creativity, 9-11 September 2024, Oxford, UK) Read the full paper Abstract: Research in Embodied Music Cognition suggests that […]
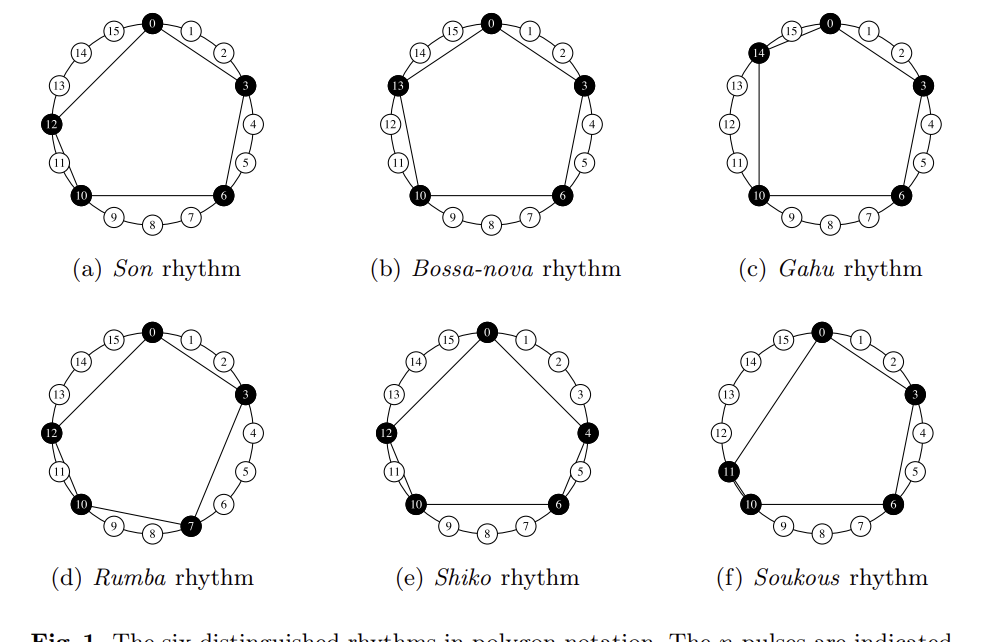
What Are « Good » Rhythms? Generating Rhythms Based on the Properties Set Out in The Geometry of Musical Rhythm
By Paul Lascabettes, Isabelle Bloch. Mathematics and Computation in Music, Jun 2024, Coimbra, Portugal. pp.45-57. Read full publication. Abstract: We propose in this article to generate good rhythms from geometric properties. This approach is based on the work by Toussaint, who investigated the properties that make a “good” rhythm good in his book The Geometry […]
Guiding Co-Creative Musical Agents through Real-Time Instrumental Playing Technique Recognition
Article by Marco Fiorini (IRCAM, Sorbonne Université, CNRS) and Nicolas Brochec (Tokyo University of the Arts) has been accepted for the SMC2024 conference (Sound and Music Computing, 4-6 July 2024, Porto, Portugal). Read the full paper Watch a video demo of the system Abstract: This paper presents a novel application and integration of a state-of-the-art CNN-based classifier for real-time […]
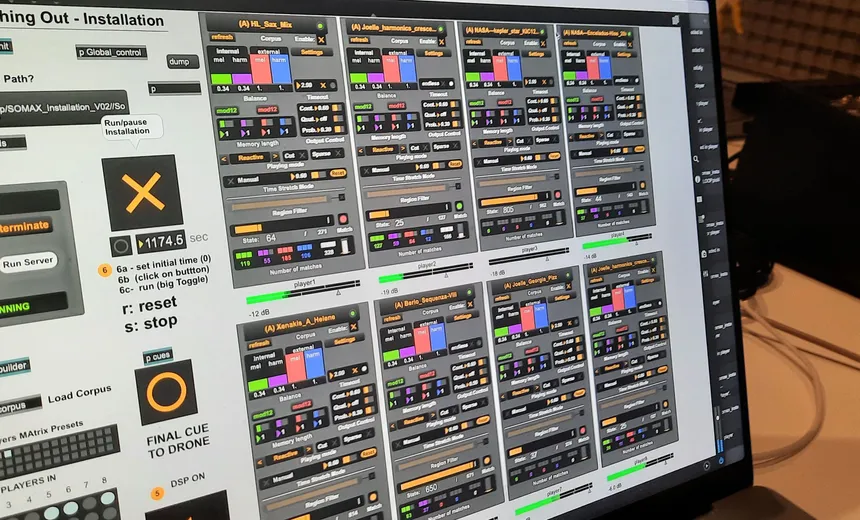
Cocreative Interaction: Somax2 and the REACH Project – The Computer Music Journal
Gérard Assayag, Laurent Bonnasse-Gahot, Joakim Borg; Cocreative Interaction: Somax2 and the REACH Project. Computer Music Journal 2022; 46 (4): 7–25. doi: https://doi.org/10.1162/comj_a_00662 https://direct.mit.edu/comj/issue/46/4 Abstract : Somax2 is an artificial intelligence (AI)-based multiagent system for human–machine “coimprovisation” that generates stylistically coherent streams while continuously listening and adapting to musicians or other agents. The model on which it is based can be […]
A.I. KOMBOÏ: RE-IMAGINING XENAKIS’ KOMBOÏ THROUGH CYBER-HUMAN CO-CREATIVE IMPROVISATION PRACTICE
Article by Marco Fiorini (IRCAM, REACH) and Lorenzo Colombo (DKDM, the Royal Danish Academy of Music) has been accepted for the JIM2024 conference (Journées d’Informatique Musicale, 6-8 May 2024, Marseille, France). Read the full paper Watch the video of the performance RésuméDans cet article, nous documentons une recherche artistique et scientifique dans laquelle nous réimaginons […]
Xenakis Komboï Reloaded by Somax2
Marco Fiorini: Somax2 interactive AI Lorenzo Colombo: percussion Recorded at the Royal Danish Academy of Music on June 6th 2023 at KLANG festival in Copenhagen
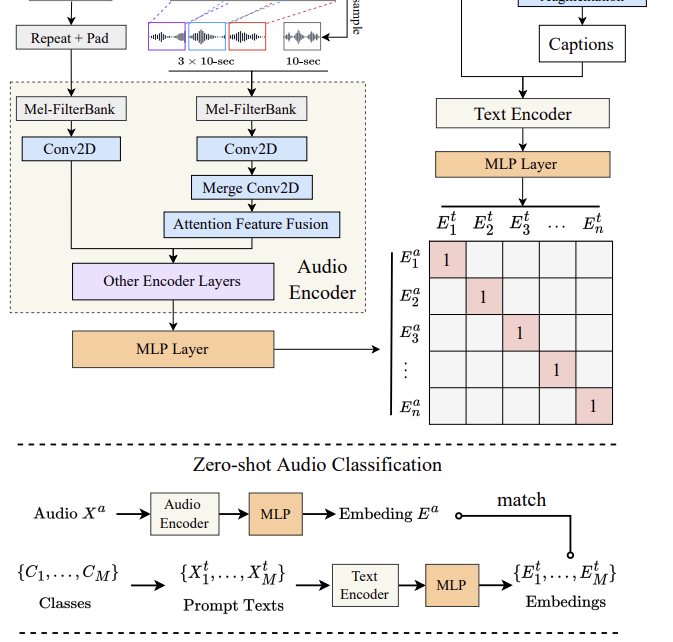
Large-scale contrastive language-audio pretraining with feature fusion and keyword-to-caption augmentation
Read full publication. Published by Yusong Wu, Ke Chen, Tianyu Zhang, Yuchen Hui, Marianna Nezhurina, Taylor Berg-Kirkpatrick, Shlomo Dubnov. Abstract: Contrastive learning has shown remarkable success in the field of multimodal representation learning. In this paper, we propose a pipeline of contrastive language-audio pretraining to develop an audio representation by combining audio data with natural […]
Challenging epistemic biases in musical AI: a guerrilla approach to human – machine comprovisation based on Xenakis’s sketches for Evryali
Article by Pavlos Antoniadis, Department of Music Studies, University of Ioannina. Download article Abstract: The objective of this paper is to reflect on the affordances of sketches as interfaces for human and machine learning, by way of a case-study based on Iannis Xenakis’s Evryali (1973). First, we report on one-to-one mappings between the composer’s original […]